Lifecycle hooks¶
PHP extensions leverage lifecycle events for common initialization or shutdown tasks. Zephir integrates with these events through hooks, primarily handled in the config.json file. The diagram illustrates the PHP Process/Request Lifecycle, depicting four types of lifecycle hooks: globals, initializers, destructors, and info. This chapter focuses on initializers and destructors.
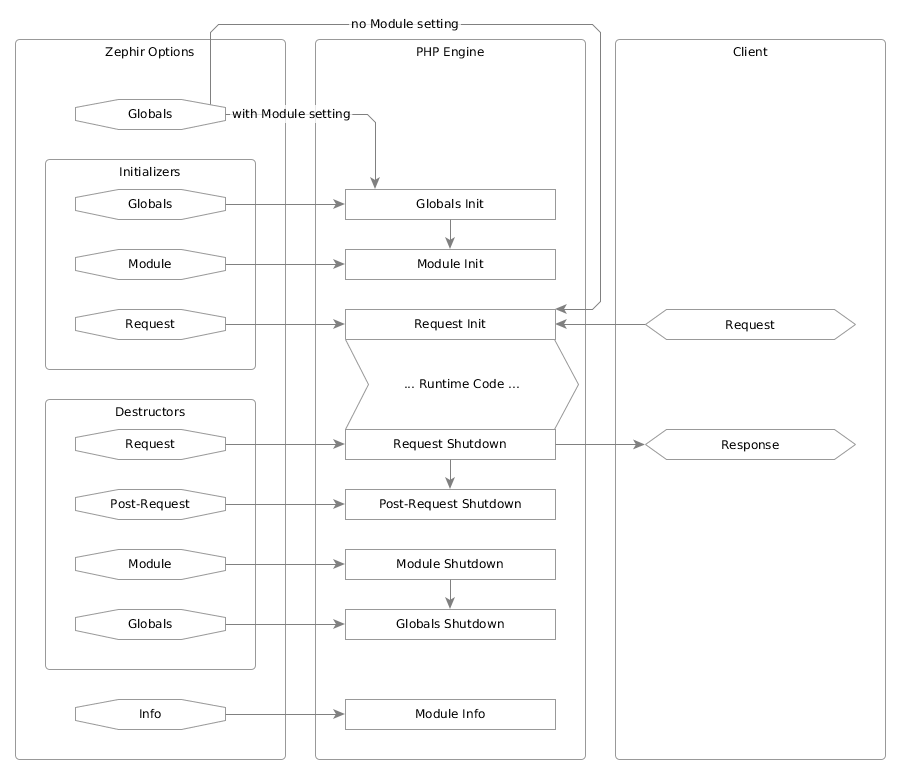
Lifecycle hooks are registered in the config.json file. As you can see in the diagram above, there are four types of lifecycle hooks - globals, initializers, destructors, and info. Each of these has its own corresponding root-level setting in the configuration, and both globals and info[phpinfo] have their own chapters. This chapter covers the other two settings.
Each hook in the config.json file is an array of objects, which themselves are essentially include/code pairs. The include value will pull in a given C header file, if it hasn't been already, so that the code will have access to its contents. The code value is the logic run by the hook itself, and while you can technically put any valid C in here, it is strongly recommended to put logic longer than one or two lines into a separate C source file (such as the one pulled in along with your included header file), and use a single-line function call here.
initializers¶
The initializers block in the config.json file includes logic for initialization events. Three key events are targeted: globals for global variable space setup, module for extension-specific initialization, and request for per-request setup.
{
"initializers": [
{
"globals": [
{
"include": "my/awesome/library.h",
"code": "setup_globals_deps(TSRMLS_C)"
}
],
"module": [
{
"include": "my/awesome/library.h",
"code": "setup_module_deps(TSRMLS_C)"
}
],
"request": [
{
"include": "my/awesome/library.h",
"code": "some_c_function(TSRMLS_C)"
},
{
"include": "my/awful/library.h",
"code": "some_other_c_function(TSRMLS_C)"
}
]
}
]
}
This configuration facilitates the execution of custom C code during the initialization process for various scopes.
destructors¶
The destructors block handles cleanup logic during shutdown events. Four events are addressed: request for finalizing data before sending a response, post-request for cleanup after sending a response, module for extension-specific cleanup, and globals for cleaning up the global variable space.
{
"destructors": [
{
"request": [
{
"include": "my/awesome/library.h",
"code": "c_function_for_shutting_down(TSRMLS_C)"
},
{
"include": "my/awful/library.h",
"code": "some_other_c_function_than_the_other_ones(TSRMLS_C)"
}
],
"post-request": [
{
"include": "my/awesome/library.h",
"code": "c_function_for_cleaning_up_after_the_response_is_sent(TSRMLS_C)"
}
],
"module": [
{
"include": "my/awesome/library.h",
"code": "release_module_deps(TSRMLS_C)"
}
],
"globals": [
{
"include": "my/awesome/library.h",
"code": "release_globals_deps(TSRMLS_C)"
}
]
}
]
}
This configuration enables the execution of custom C code during various shutdown events, ensuring proper cleanup and finalization processes.